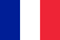
Cervical osteochondrosis is the progressive dyne and deigenerative lesion of the intervertebral discs in the area of 1-7 vertebrae belonging to the cervical region.
As a result of cervical osteochondrosis, deformation, exhaustion and then damage to vertebral bodies occurs. This disrupts normal blood supply and nerve conductivity to the neck and in those areas that are internal from the roots of the cervical nerves.
Cervical osteochondrosis can be isolated or combined with osteochondrosis of other departments - lumbar and sacral.
Reason
The causes of dystrophic and degenerative changes in the intervertebral discs have not yet been properly studied. The assumption that osteochondrosis is an elderly phenomenon of confirmation. It is also found in children and adolescents.
There are a number of factors that predisposition to the development of osteochondrosis. These include:
Symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis
The cervical spine, due to the features of the skeleton, justice, and due to the large size of the head, is particularly susceptible to the development of osteochondrosis-rhusa in it are smaller compared to other parts of the spine, and the muscle frame is not very pronounced.
The most characteristic symptoms that patients complain of - pain in the cervical region. Depending on the damage area, the pain may be located
Pain for cervical osteochondrosis is due to the features of the cervical region.
The first signs of cervical osteochondrosis are irrelevant and slightly specific:
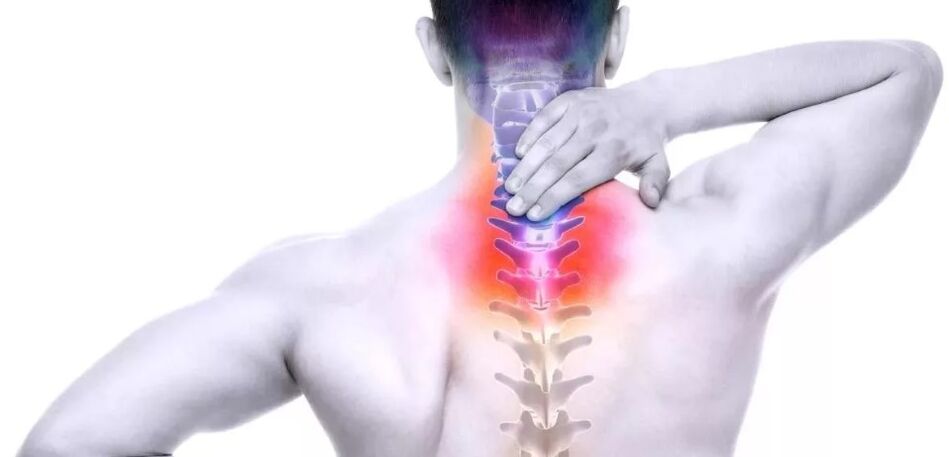
Main symptoms:
Vegetative
Since the vertebral arteries are compressed, neurological manifestations are observed: headaches, nausea, pallor.
Spinal symptom
The pain localizes after the sternum to the left.
This type of pain should be distinguished by pain such as angina pectoris (with angina pectoris, nitroglycerin relieved, with osteochondrosis - no).
With a gradual violation of the structure of the intervertebral discs, their compression (compression) occurs and the violation of the roots of the nerves occurs, as well as the narrowing or violation of the arteries and veins, which occur in the area of vertebral bodies.
This leads to the formation of special - radical and ischemic syndromes.
Disordisms of circulatory disorders due to compression of vessels in the area of cervical vertebrae give headaches to migraine, severe dizziness, visual damage and ears, fly flies before the eyes, disorders of autonomous functions.

There may be manifestations of cardiac syndrome with compressive heart pain, lack of air and heartbeat, rhythm disorders.
Complications
The serious complications of cervical osteochondrosis are
Troubleshooting
In the presence of the above complaints, an appeal is needed for the doctor or orthopedic neurologist.
First of all, the doctor will evaluate movement and pain in the neck, sensitivity and other functions. Then, if necessary, the cervical spine radiography in several projections, if necessary, the calculated tomography or the magnetic resonance scan with the suspicion of hernia.
In case of circulatory disorders, reoencephalography and fundus examination will be needed.
Treatment of cervical osteochondrosis
Today, there are also traditional and non -traditional methods for the treatment of osteochondrosis in the cervical spine.
Conservative methods are mainly used:

In the treatment of cervical osteochondrosis, substances that restore the structure of the intervertebral discs - chondroprotectors are used.
The course of vitamin B of Group B is indicated, external products for therapy are applicable - gel and ointments, creams with anti -inflammatory and analgesic ingredients. Shows stimulants of intervertebral discs regeneration.
Exceeded and general massage, acupuncture, physiothecept, physiotherapy and gymnastics and gymnastics helps treat osteochondrosis. The method of osteopathy is well proven - a mild effect on the "captured" areas of the muscles and beads.
In the treatment of cervical osteochondrosis, wearing a special collar (black collar) is recommended.
Complications of cervical osteochondrosis with hernia that violate sensitivity and blood circulation can be treated immediately.
The duration of treatment depends on the negligence of the condition, as osteochondrosis is a chronic progressive disease. Treatment can be long, and preventive courses are performed for life.
Proper nutrition will help relieve osteochondrosis.
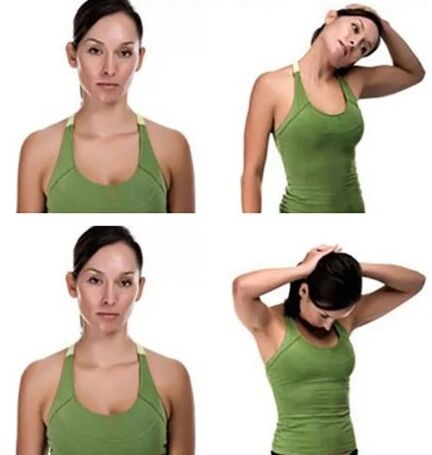
Exercises for the treatment of cervical osteochondrosis:
PREVENTION
The basis of cervical backpack is a strong and healthy spine, physical activity, a comfortable bed with anatomical pillows and mattresses, proper behavior and proper nutrition.
It is worth avoiding neck damage and lifting weight. It is necessary to combine prolonged landing with periods of rest and warm.